-
前列腺癌日趋年轻化,是危害男性健康的疾病之一[1]。前列腺癌演化进展与基因异常表达有关[2-3]。驱动蛋白-5(Eg5)基因增高通过干扰纺锤体组装进而影响染色体的动态平衡,促进肿瘤增殖[4-5],丝氨酸苏氨酸激酶-1(PIM-1)增高表达促进肿瘤细胞增殖、侵袭和细胞周期改变[6-7]。对肿瘤Oncomine数据库进行检测验证发现,PIM-1和Eg5基因在前列腺癌发生进展中有相关性,但它们在前列腺癌中的作用尚不清楚。本研究采用免疫组化SP法检测前列腺癌中PIM-1和Eg5蛋白表达,探讨与前列腺癌临床病理特征之间的关系及相关性。
-
1 资料与方法
-
1.1 一般资料
-
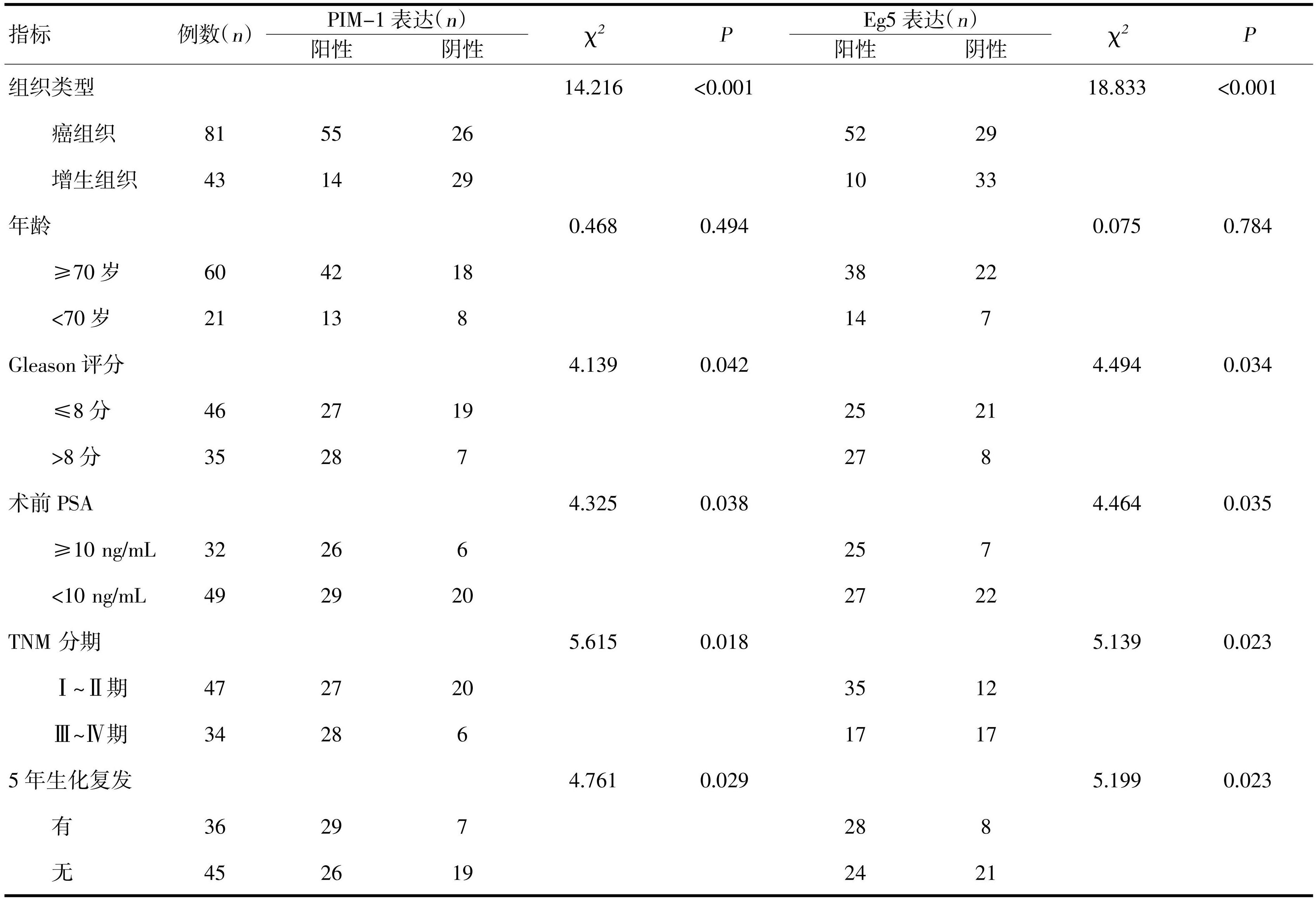
选取2016年1月—2017年6月浙江大学医学院附属金华医院/金华市中心医院泌尿外科收治的81例前列腺癌患者,年龄49~83岁,平均67.1岁;选取同期收治的43例前列腺增生患者,年龄48.5~84岁,平均66.9岁,采用Gleason分级评价其分化程度,Gleason评分≤8分的46例,Gleason评分>8分的35例。按照2002年AJCC临床TNM分期标准,Ⅰ~Ⅱ期47例,Ⅲ~Ⅳ期34例。所有前列腺癌患者术前均未接受放疗、化疗和内分泌治疗。所有参与研究的患者均在本院签知情同意书。
-
1.2 采用免疫组化法检测PIM-1和Eg5蛋白表达水平
-
免疫组化染色所用SP试剂盒和DAB 显色剂均为北京中杉金桥生物技术有限公司产品,货号:SP0041-18 mL。实验按照试剂盒说明书进行。所有标本经10%甲醛固定,石蜡包埋,3 µm厚连续切片,以3%过氧化氢溶液室温孵育10 min,常规封闭,后由二甲苯进行脱蜡后,依次梯度乙醇水化。加入兔抗人Eg5一抗(浓度1:100,规格:100 µL,货号:CSB-PA182810,购于武汉博士德公司),4℃孵育过夜,PBS洗3次,每次5 min;滴加二抗(生物素标记)室温孵育30 min;PBS洗3次,每次5 min;经DAB显色,苏木素复染,最后封片、光镜观察,并使用PBS缓冲液代替一抗作为阴性对照;PIM-1免疫组化实验同Eg5,PIM-1为兔抗人多克隆抗体(浓度1:150,规格:100 µg,货号:3787R-100)。
-
1.3 免疫组化染色结果判定
-
PIM-1和Eg5蛋白主要定位表达在细胞质,而在胞浆及胞核中少量表达。根据高倍镜下100个细胞中阳性表达细胞数判断免疫组化结果:(-)为阴性,阳性细胞表达细胞数<10%为(+),阳性表达细胞数10%~25%(++),阳性表达细胞数25%~50%为(+++),>50%为(++++),阳性细胞数在(+++)以上为PIM-1和Eg5蛋白表达阳性(+)。
-
1.4 统计学处理
-
采用 SPSS 26.0 进行统计分析,计数资料以例表示,比较采用χ2检验,相关性分析采用Pearson相关性分析,以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
-
2 结果
-
2.1 PIM-1和Eg5 蛋白在前列腺癌中的表达情况
-
免疫组化染色结果发现,PIM-1蛋白和Eg5蛋白主要表达在细胞质,而在细胞膜中少量表达。见图1。
-
图1 PIM-1和Eg5蛋白在前列腺癌和前列腺增生中的表达
-
2.2 PIM-1和Eg5在前列腺癌表达与前列腺癌患者临床病理特征之间的关系
-
PIM-1蛋白在前列腺癌中表达阳性率为67.90%(55/81),在前列腺增生中表达阳性率为32.56%(14/43),差异有统计学意义(P<0.01)。Eg5蛋白在前列腺癌中表达阳性率为64.20%(52/81),在前列腺增生中表达阳性率为23.26%(10/43),差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);PIM-1蛋白在前列腺癌Gleason≤8分表达阳性率为58.70%(27/46),在Gleason>8分表达阳性率为80.00%(28/35),差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。Eg5在前列腺癌Gleason≤8分的表达阳性率为54.35%(25/46),在Gleason>8分表达阳性率为77.14%(27/35),差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);在Ⅰ~Ⅱ期表达率74.47%(35/47)和Ⅲ~Ⅳ期阳性表达率为50.00%(17/34),差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);Eg5在前列腺癌5年生化复发表达阳性率为77.78%(28/36),在5年无生化复发表达阳性率为53.33%(24/45),差异有统计学意义。见表1。
-
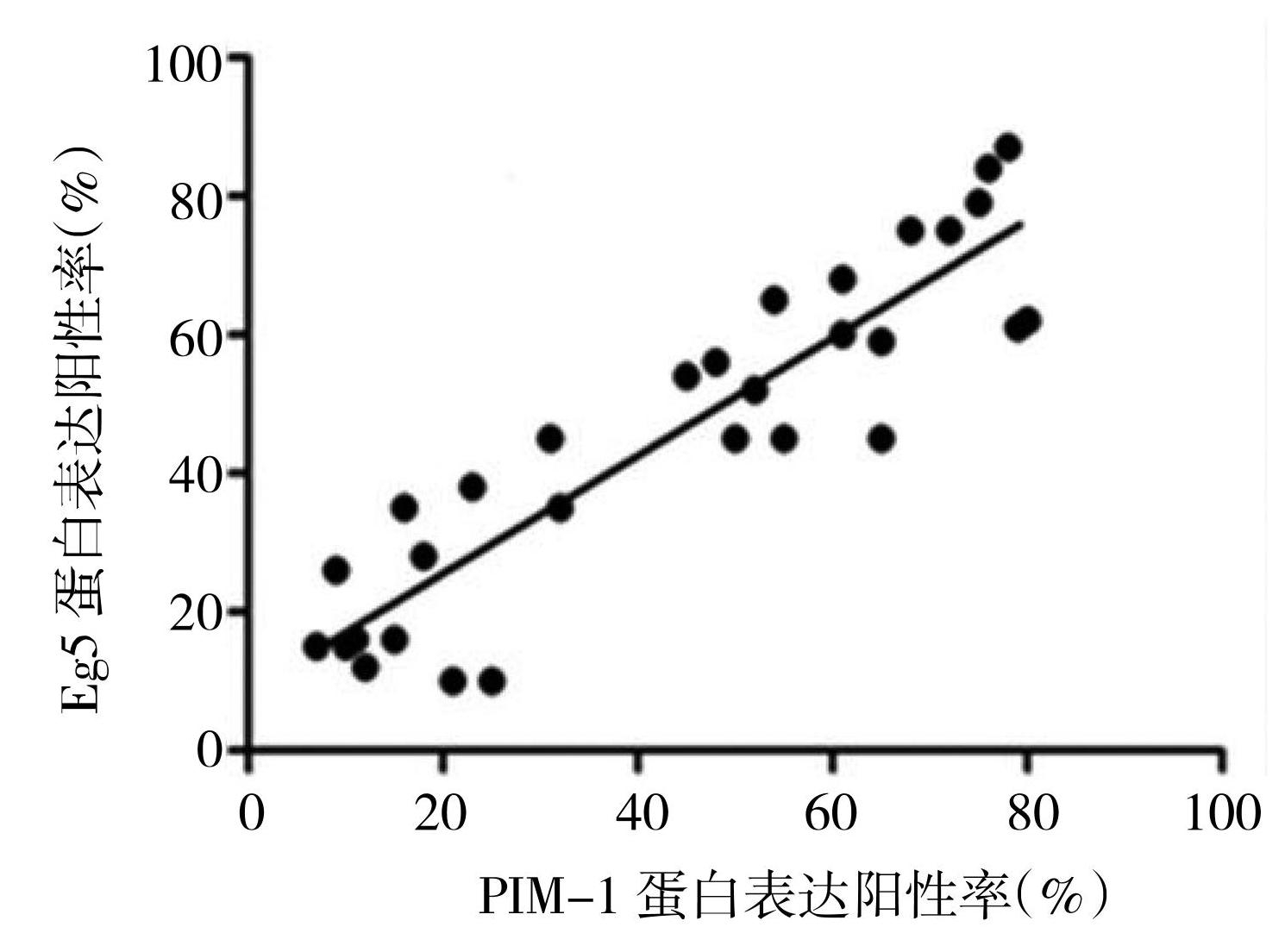
2.3 PIM-1与Eg5蛋白在前列腺癌中表达情况的Pearson相关性分析
-
在前列腺癌中,PIM-1与Eg5蛋白表达阳性率呈正相关(r=0.825,P<0.05)。
-
图2 前列腺癌中PIM-1和Eg5蛋白表达的相关性分析
-
3 讨论
-
前列腺癌起病隐匿,发生机制复杂,进展后发展快,前列腺癌是与基因有关的疾病[8]。PIM-1激酶是丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶家族成员一员,在癌症的进展和发展中起着非常重要的作用[9],有研究支持抑制PIM-1是抑制肿瘤细胞增殖的有效途径[10];PIM-1激酶增高表达在各种类型的癌症中,包括膀胱癌、胰腺癌、乳腺癌等[11-13]。在前列腺癌中虽然PIM-1呈现过度表达,但其在前列腺癌中作用的研究远未清楚。Eg5基因是细胞有丝分裂周期中一个重要的驱动蛋白基因,在细胞分裂中起重要作用[14];Eg5过度表达会干扰纺锤体构建,使纺锤体形成受到影响[15]。相关研究已经证实,Eg5增高可促进肿瘤细胞增殖和侵袭 [16-17];但在前列腺癌中PIM-1与Eg5表达相关性未见报道。
-
本研究采用免疫组化法对前列腺癌中PIM-1和Eg5蛋白的表达状况及相关性进行研究,结果发现前列腺癌中PIM-1和Eg5蛋白呈现增高表达,它们的增高表达与前列腺癌临床分期和Gleason分级、术前PSA、5年生化复发有关,与患者年龄无关。Eg5参与免疫调节与T细胞有关,阻断了CD4阳性T淋巴细胞可导致细胞死亡[18];更进一步研究发现Eg5也对蛋白质翻译、癌细胞迁移、神经元存活和新生血管生成中有重要作用[19-20]。然而,现有的研究仅仅提示Eg5可能在肿瘤的发生演化中扮演着重要的作用,在前列腺癌中是否有相同的作用需要进一步体内外研究证实。有研究对Eg5在膀胱癌细胞系研究中显示,膀胱癌T24细胞株中Eg5增高表达的Eg5促进了膀胱癌T24细胞的增殖和迁移,靶向沉默Eg5有效地抑制了膀胱癌T24细胞增殖与迁移[21],但对其确切的机制并未进一步深入研究。
-
前列腺癌中PIM-1增高表达与其临床相关性已经得到证实,PIM-1抑制剂可以明显抑制前列腺细胞增殖和侵袭,PIM-1抑制剂可能通过多种肿瘤抑制途径有效抑制肿瘤细胞增殖[22];本研究对PIM-1与Eg5蛋白在前列腺癌中表达相关性进行了研究,发现在前列腺癌中二者呈正相关,说明它们在前列腺癌中共同作用于前列腺癌的发生和进展。
-
总之,PIM-1与Eg5蛋白在前列腺癌中呈现高表达,这种高表达共同引发前列腺肿瘤发生和进展;但PIM-1与Eg5在前列腺癌中确切的作用机制未明,有必要进一步采用体内及体外实验研究它们在前列腺癌细胞系中的表达模式及作用方式,为前列腺癌的治疗探寻一条新靶向治疗的有效指标。
-
参考文献
-
[1] Global Burden of Disease Cancer Collaboration,Fitzmaurice C,Akinyemiju TF,et al.Global,regional,and national cancer incidence,mortality,years of life lost,years lived with disability,and disability-adjusted life-years for 29 cancer groups,1990 to 2016:a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study[J].JAMA Oncol,2018,4(11):1553-1568.
-
[2] Bicker A,Nauth T,Gerst D,et al.The role of myoglobin in epithelial cancers:insights from transcriptomics[J].Int J Mol Med,2020,45(2):385-400.
-
[3] Xu W,Huang MH,Guo J,et al.The role of CHK1 varies with the status of oestrogen-receptor and progesterone-receptor in the targeted therapy for breast cancer[J].Int J Biol Sci,2020,16(8):1388-1402.
-
[4] Raghav D,Sebastian J,Rathinasamy K.Biochemical and Biophysical characterization of curcumin binding to human mitotic kinesin Eg5:insights into the inhibitory mechanism of curcumin on Eg5[J].Int J Biol Macromol,2018,109:1189-1208.
-
[5] She ZY,Zhong N,Yu KW,et al.Kinesin-5 Eg5 is essential for spindle assembly and chromosome alignment of mouse spermatocytes[J].Cell Div,2020,15:6.
-
[6] Ziemianowicz DS,MacCallum JL,Schriemer DC.Correlation between labeling yield and surface accessibility in covalent labeling mass spectrometry[J].J Am Soc Mass Spectrom,2020,31(2):207-216.
-
[7] Chen CM,Wang ZY,Zhang JH,et al.Dextran-conjugated caged siRNA nanoparticles for photochemical regulation of RNAi-induced gene silencing in cells and mice[J].Bioconjug Chem,2019,30(5):1459-1465.
-
[8] Miyahira AK,Sharp A,Ellis L,et al.Prostate cancer research:the next generation;report from the 2019 Coffey-Holden Prostate Cancer Academy Meeting[J].Prostate,2020,80(2):113-132.
-
[9] Ledet RJ,Ruff SE,Wang Y,et al.Identification of PIM1 substrates reveals a role for NDRG1 phosphorylation in prostate cancer cellular migration and invasion[J].Commun Biol,2021,4(1):36.
-
[10] Ashrafizadeh M,Paskeh MDA,Mirzaei S,et al.Targeting autophagy in prostate cancer:preclinical and clinical evidence for therapeutic response[J].J Exp Clin Cancer Res,2022,41(1):105.
-
[11] Ruff SE,Vasilyev N,Nudler E,et al.PIM1 phosphorylation of the androgen receptor and 14-3-3 ζ regulates gene transcription in prostate cancer[J].Commun Biol,2021,4(1):1221.
-
[12] Xu JW,Xiong GB,Cao Z,et al.PIM-1 contributes to the malignancy of pancreatic cancer and displays diagnostic and prognostic value[J].J Exp Clin Cancer Res,2016,35(1):133.
-
[13] Mirosława K,Zygmunt K,Andrzej O.Antitumor activity of the protein kinase inhibitor 1-(β-D-2’-deoxyribofuranosyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrabromo-1H-benzimidazole in breast cancer cell lines[J].BMC Cancer,2022,22(1):1069.
-
[14] VukušićK,Ponjavić I,Buđa R,et al.Microtubule-sliding modules based on kinesins EG5 and PRC1-dependent KIF4A drive human spindle elongation[J].Dev Cell,2021,56(9):1253-1267.e10.
-
[15] Chen GY,Kang YJ,Gayek AS,et al.Eg5 inhibitors have contrasting effects on microtubule stability and metaphase spindle integrity[J].ACS Chem Biol,2017,12(4):1038-1046.
-
[16] Sturgill EG,Norris SR,Guo Y,et al.Kinesin-5 inhibitor resistance is driven by kinesin-12[J].J Cell Biol,2016,213(2):213-227.
-
[17] Shao YY,Sun NY,Jeng YM,et al.Eg5 as a prognostic biomarker and potential therapeutic target for hepatocellular carcinoma[J].Cells,2021,10(7):1698.
-
[18] Liu M,Li DW,Sun L,et al.Modulation of Eg5 activity contributes to mitotic spindle checkpoint activation and Tat-mediated apoptosis in CD4-positive T-lymphocytes[J].J Pathol,2014,233(2):138-147.
-
[19] Olvera-García G,Aguilar-García T,Gutiérrez-Jasso F,et al.A transcriptome-based model of central memory CD4 T cell death in HIV infection[J].BMC Genomics,2016,17(1):956.
-
[20] Ricci A,Cataldi A,Carradori S,et al.Kinesin Eg5 selective inhibition by newly synthesized molecules as an alternative approach to counteract breast cancer progression:an in vitro study[J].Biology(Basel),2022,11(10):1450.
-
[21] Müller K,Klein PM,Heissig P,et al.EGF receptor targeted lipo-oligocation polyplexes for antitumoral siRNA and miRNA delivery[J].Nanotechnology,2016,27(46):464001.
-
[22] Nikolakis D,Garantziotis P,Sentis G,et al.Restoration of aberrant gene expression of monocytes in systemic lupus erythematosus via a combined transcriptome-reversal and network-based drug repurposing strategy[J].BMC Genomics,2023,24(1):207.
-
摘要
目的:检测前列腺癌中丝氨酸苏氨酸激酶-1(PIM-1)和驱动蛋白-5(Eg5)蛋白表达,探讨其表达与前列腺癌临床病理及它们之间的相关性。方法:采用免疫组化SP法检测81例前列腺癌和43例前列腺增生组织中PIM-1和Eg5蛋白表达水平,卡方检验分析PIM-1和Eg5蛋白表达阳性率与前列腺癌的临床病理特征之间的关系,采用Pearson相关分析PIM-1和Eg5蛋白在前列腺癌中的相关性。结果:PIM-1和Eg5蛋白在前列腺癌中表达增高,明显高于前列腺增生,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),PIM-1和Eg5蛋白表达阳性率与Gleason评分、临床分期、术前PSA和5年生化复发有关(P<0.05);与患者年龄无关(P>0.05)。PIM-1和Eg5蛋白表达阳性率高的生化复发率高于PIM-1和Eg5蛋白表达阳性率低的患者 (P<0.05),Pearson相关性分析显示,前列腺癌中PIM-1和Eg5蛋白呈正相关(r=0.825,P<0.05)。结论:PIM-1和Eg5基因可能与前列腺癌演化和进展有关,二者联合检测有望提高对前列腺癌的预测能力。
Abstract
Objective To detect the expression of serine threonine kinase-1(PIM-1) and kinesin-5 (Eg5) proteins in prostate cancer and to investigate their correlation with the clinicopathology of prostate cancer. Methods The expression of PIM-1 and Eg5 protein in 81 cases of prostate cancer and 43 cases of benign prostatic hyperplasia were detected by immunohistochemical streptavidin-perosidase method. The relationship between the positive rate of PIM-1 and Eg5 protein expression and the clinicopathological characteristics of prostate cancer were analyzed by chi square test. The correlation between PIM-1 and Eg5 protein in prostate cancer was evaluated by Pearson correlation analysis. Results The expressions of PIM-1 and Eg5 proteins in prostate cancer were significantly higher than those in benign prostatic hyperplasia (P<0.05). The positive rates of PIM-1 and Eg5 protein expressions were related to Gleason score, clinical stage, preoperative PSA and 5-year biochemical recurrence (P<0.05). They were not related to the patient's age (P>0.05). Biochemical relapse with high positive rate of PIM-1 and Eg5 protein expression was higher than that with low positive rate of PIM-1 and Eg5 protein expression (P<0.05). Pearson correlation analysis showed that PIM-1 and Eg5 proteins were positively correlated in prostate cancer (r=0.825, P<0.05). Conclusions PIM-1 and Eg5 genes may be related to the evolution and progression of prostate cancer, and joint detection may improve the prediction of prostate cancer.
关键词
前列腺癌 ; 丝氨酸苏氨酸激酶-1 ; 驱动蛋白-5 ; 免疫组织化学
Keywords
Prostate cancer ; serine threonine kinase-1 ; kinesin-5 ; immunohistochemistry